 Remove Plaque Build-Up in Arteries
Remove Plaque Build-Up in Arteries
MEDIUM CHAIN TRIGLYCERIDES (MCTs) Overview Information 
Medium chain triglycerides (MCTs) are partially man-made fats. The name refers to the way the carbon atoms are arranged in their chemical structure. MCTs are generally made by processing coconut and palm kernel oils in the laboratory. Usual dietary fats, by comparison, are long-chain triglycerides. People use MCTs as medicine.
MCTs are used along with usual medications for treating food absorption disorders including diarrhea, steatorrhea (fat indigestion), celiac disease, liver disease, and digestion problems due to partial surgical removal of the stomach (gastrectomy) or the intestine (short bowel syndrome).
MCTs are also used for “milky urine” (chyluria) and a rare lung condition called chylothorax. Other uses include treatment of gallbladder disease, AIDS, cystic fibrosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and seizures in children.
Athletes sometimes use MCTs for nutritional support during training, as well as for decreasing body fat and increasing lean muscle mass.
MCTs are sometimes used as a source of fat in total parenteral nutrition (TPN). In TPN, all food is delivered intravenously (by IV). This type of feeding is necessary in people whose gastrointestinal (GI) tract is no longer working.
Intravenous MCTs are also given to prevent muscle breakdown in critically ill patients.
Other Names:
Propanetriol Trioctanoate, AC-1202, Acide Caprique, Acide Caproïque, Acide Caprylique, Acide Laurique, Capric Acid, Caproic Acid, Caprylic Acid, Caprylic Triglycerides, Lauric Acid, MCT, MCT’s, MCTs, Medium-Chain Triacylglycerols, Medium-Chain Triglycerides, TCM, Triacylglycérols à Chaîne Moyenne, Tricaprylin, Triglycérides à Chaîne Moyenne, Triglycérides Capryliques, Triglicéridos de Cadena Media (TCMs), Trioctanoin.
How does it work?
MCTs are a fat source for patients who cannot tolerate other types of fats. Researchers also think that these fats produce chemicals in the body that might help fight Alzheimer’s disease.
MCTs in Food
The main natural source of MCTs in foods is coconut, especially in coconut oil. Palm kernel oil, which should not be confused with palm oil, is also a big source of MCTs. Butter is also a source of MCTs, but to a smaller extent compared to coconut and palm kernel oil. MCTs, mainly from coconut oil, can be extracted and concentrated to produce MCT oil, which are available in most health food stores. Human milk is rich in MCTs and this is why concentrated sources of MCTs are commonly added to infant formulas.
Bonus: The health benefits of red palm fruit oil can be achieved by incorporating only 1-2 tablespoons into your daily diet.
Red Palm Fruit Oil vs. Palm Kernel Oil
Regarded as a sacred healing food by many civilizations, including the ancient Egyptians, crude or virgin red palm fruit oil should be regarded as one of the most nutritious edible oils in the world. It is not to be confused with palm kernel oil. It is derived from the fruit of the oil palm tree (Elaeis guineensis) and is referred to as “red palm oil” because of its rich dark red color in its unprocessed natural state. Palm kernel oil is derived from the seed or the kernel.
At room temperature, this semi-solid oil seems as likely as lard to clog your arteries. But what might shock you to learn, as it has equally stunned researchers, is that although red palm fruit oil is indeed high in saturated fat, it actually protects against heart disease. Saturated fats behave like a thick molasses through the cardiovascular system, eventually contributing to plaque (atherosclerosis). But studies show that adding palm oil into the diet can remove plaque build-up in arteries and, therefore, reverse the process of plaque and prevent blockages. In fact, studies funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have shown that a natural form of vitamin E called alpha tocotrienol, which is the form found in high amounts in red palm fruit oil, can help reduce the effects of stroke by 50% by protecting your brain’s nerve cells.
Removing plaque is not the only way red palm oil may protect against strokes and heart attacks. Red palm oil can also improve cholesterol values and also helps maintain proper blood pressure. Science now understands that inflammation in the artery lining is what warrants cholesterol to deposit in the first place. So, it makes sense that the protective effects come from the high antioxidant, anti-inflammatory content of the red palm oil which works to quench free radicals and keep inflammation under control.
Palm fruit oil contains mainly palmitic and oleic acids and is about 50% saturated, while palm kernel oil contains mainly lauric acid and is more than 89% saturated. The general assumption that kernel oil and palm fruit oil are one in the same may have lead to one of the greatest oversights in modern nutrition. The stigma attached to the kernel has kept the fruit in the dark – at least until now. Virgin organic sustainable red palm fruit oil is otherwise a bona fide miracle food.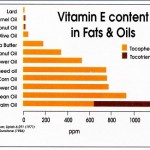
Palm kernel oil does not convey the same health benefits that Red Palm Fruit Oil does. The health benefits are only achieved due to the red color of the palm fruit oil that is attributed to its high content of carotenes, which include beta-carotene and lycopene. These powerhouse antioxidant nutrients are the same ones that give tomatoes and carrots and other fruits and vegetables their rich red and orange colors. What may shock you is that red palm fruit oil contains more than tomatoes or carrots. Red palm fruit oil is also densely packed with numerous tocotrienols – a powerful form of vitamin E.
MCTs and Weight
MCTs are metabolized differently compared to the long-chain triglycerides found in vegetable oils and animal fats. When you eat foods containing MCTs, these fats can bypass many digestive steps and go straight to your liver. Compared to other fats, MCTs are burned for energy by your body and not stored as fat, as explained by Dr. Mary G. Enig, a biochemist, in his book “Know Your Fats.” Moreover, MCTs provide slightly less calories compared to other fats, in addition to reducing your appetite and increasing your metabolism, which are all important factors that can contribute to a healthier weight.
MCTs and Other Properties
Once you ingest MCTs, they can have anti-microbial properties in your body. MCT-rich foods can help protect you against viruses, bacteria and parasites. Studies have also indicated a role for MCTs in slowing aging, improving physical performance, boosting immunity, lowering blood sugar levels and preventing heart diseases, according to “Nutrition Reviews.”
MCTs in Your Diet
To include more MCTs in your diet, use coconut oil instead of your usual fats and oils. Virgin coconut oil is less chemically processed and has a pleasant coconut flavor that can enhance many dishes. Use coconut oil to cook your eggs, vegetables and meat. You can also substitute oils and margarine for coconut oil when baking muffins, granola bars and cookies. You can even add coconut oil to your green tea if you like. Fresh coconut meat, unsweetened dessicated coconut, coconut milk, coconut butter and coconut cream also provides MCTs, but in smaller quantities compared to coconut oil. Talk to your physician before making major changes to your diet or attempting to treat any health conditions.
Read more: http://www.livestrong.com/article/517455-which-foods-contain-mcts/#ixzz2bEFRxTiK
http://www.hybridrastamama.com/2012/08/333-Uses-For-Coconut-Oil.html